How to integrate VG in silverlight application/site
To integrate Visual Guard in your WCF Silverlight service you have to:
- Add the assemblies of Visual Guard as references of your project.
- Add an authentication service.
- Modify the "web.config" or the "app.config" file of your application to integrate the Visual Guard module.
- Integrate Visual Guard in the code of your application.
- Create a Visual Guard repository and declare your application using the Visual Guard console. This repository will contain all security items (users, roles, permissions ...) of your application.
- Allow anonymous sessions,
- Generate the Visual Guard configuration files by using the Visual Guard console. These configuration files will be needed to connect your application to the repository.
- Grant read/write permissions to the repository.
Referencing Visual Guard assemblies
In order to use Visual Guard, you must add references to Visual Guard assemblies:
- Open the solution of your project in Visual Studio.
- In the solution explorer, expand the project node.
- Right-click the Project node for the project and select Add Reference from the shortcut menu.
- In the .Net tab, select the 4 assemblies Novalys.VisualGuard.Security, Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.WebForm, Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.WebService, Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.<RepositoryType> (File, SQLServer or Oracle). Click the Select button, and then click the OK button
Note: In the list of assemblies, Visual Studio can display different versions of the Visual Guard assemblies. You must select the assembly corresponding to the version of the framework used in your project.
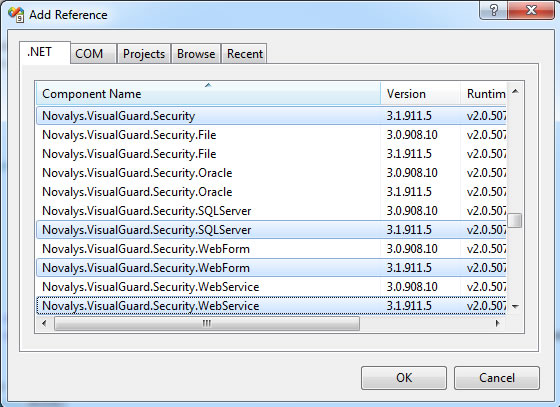
If the assemblies do not appear in this list, you can use the Browse tab and select them in the directory <Visual Guard installation directory>/bin/3.1
Description of Visual Guard assemblies:
- Novalys.VisualGuard.Security contains the main Visual Guard classes.
- Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.Files contains the classes needed to access a file based repository.
- Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.SQLServer contains the classes needed to access a repository stored in a Microsoft SQLServer database (SQLServer 2000 or higher). Available only in Visual Guard Enterprise Edition
- Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.Oracle contains the classes needed to access a repository stored in an Oracle database (8i or higher). Available only in Visual Guard Enterprise Edition
- Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.WebForm contains the classes needed for ASP.Net applications. You must reference this assembly in the ASP.Net WebSite or the ASP.Net WebService project.
- Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.WebService contains the classes needed for application hosting WCF services. You must reference this assembly in all projects hosting WCF services that contain the classes needed for application hosting WCF services. You must reference this assembly in all projects hosting WCF services that need to be secured by Visual Guard.
Use the authentication User Name / Password
Create an authentication service
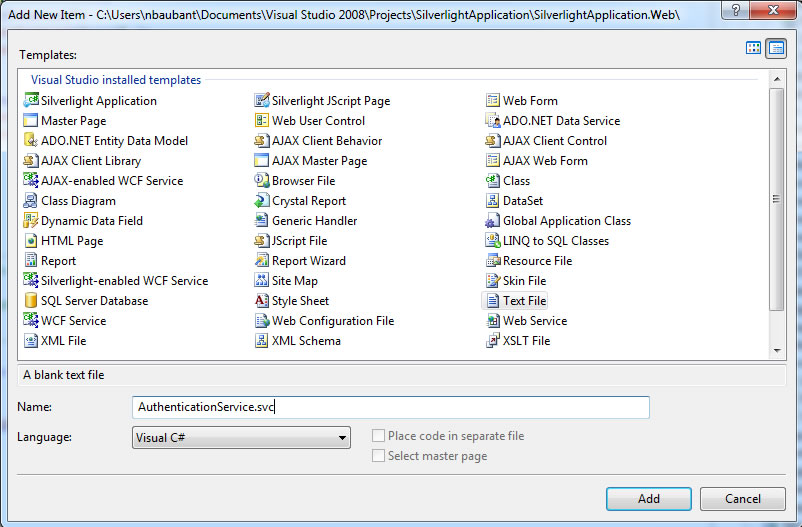
To expose the ASP.NET Authentication system, you have to add a new WCF service. Since we will point this at the default WCF service that ships with ASP.NET, we don't need any code behind. The simplest approach is to add a new Text File.
In the ASP.NET website:
- Add New Item,
- Select Text File
- And call it "AuthenticationService.svc"
Add this one line as the contents of the file. This connects it to the implementation that ships as part of ASP.NET
<%@ ServiceHost Language="C#" Service="System.Web.ApplicationServices.AuthenticationService" %>
Modifying the "app.config" or "web.config" file of your application
To enable Visual Guard and the authentication in your application, you must declare and configure the section class <system.serviceModel> of your application hosting your WCF services.
Add the authentication service
In Web.config, we need to add the WCF magic to turn the service on.
In text editor:
<system.serviceModel>
<services>
<service behaviorConfiguration="AuthenticationServiceTypeBehaviors" name="System.Web.ApplicationServices.AuthenticationService">
<endpoint binding="basicHttpBinding" bindingConfiguration="userHttp" bindingNamespace="http://asp.net/ApplicationServices/v200" contract="System.Web.ApplicationServices.AuthenticationService" />
</service>
</services>
</system.serviceModel>
<system.serviceModel> <bindings>
<basicHttpBinding>
<binding name="userHttp">
<security mode="None">
<transport>
<extendedProtectionPolicy policyEnforcement="Never" />
</transport>
</security>
</binding>
</basicHttpBinding>
</bindings> </system.serviceModel>
<system.serviceModel> <behaviors>
<serviceBehaviors>
<behavior name="AuthenticationServiceTypeBehaviors">
<serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled="true" />
</behavior> </serviceBehaviors>
</behaviors> </serviceHostingEnvironment aspNetCompatibilityEnabled="true" /> </system.serviceModel>
We need to enable authentication to be exposed via the web service.This is done by adding a System.Web.Extensions section.
<system.web.extensions>
<scripting>
<webServices>
<authenticationService enabled="true" requireSSL="false"/>
</webServices>
</scripting>
</system.web.extensions>
Configuring User Name Authentication
<authentication mode="Forms"/>
Configuring VGHTTPModule
To enable Visual Guard in your application, you must declare the class Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.WebForm.VGHttpModule in the list of HttpModules in the "web.config" of your application. To do that, you must:
- Add the following line of code in the <HttpModules> node.
<add type="Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.WebForm.VGHttpModule,Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.WebForm" name="VGModule"/>
For example:
<configuration> <system.web> ... <httpModules> <add type= "Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.WebForm.VGHttpModule,Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.WebForm" name="VGModule"/> </httpModules> ... </system.web> </configuration>
This module will enable Visual Guard in your application. It will automatically detect the type of authentication used in your application. Visual Guard supports Forms, Windows and Passport authentication.
If you use Windows or Passport authentication mode, Visual Guard will automatically detect the authenticated user.
If the user does not have a role in the application, or if the user is not declared in the repository, or if the user is anonymous, Visual Guard will deny the user access to all methods of your service.
Configuring Membership
Visual Guard is fully compatible with Membership API. To use Membership features, you must declare VGMembershipProvider and VGRoleProvider in your web.config file.
<configuration> <system.web> ... <roleManager defaultProvider="VGRoleProvider" enabled="true"> <providers> <add name="VGRoleProvider" type="Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.WebForm.VGRoleProvider, Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.WebForm" /> </providers> </roleManager> ... <membership defaultProvider="VGMemberShipProvider"> <providers> <add name="VGMemberShipProvider" type="Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.WebForm.VGMemberShipProvider, Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.WebForm" /> </providers> </membership> ... </system.web> </configuration>
Call the authentication service in Silverlight
To call the authentication method in your silverlight application, you have to:
- Add the Authentication service in your Silverlight application,
- call the login method.
Add the authentication service to your project
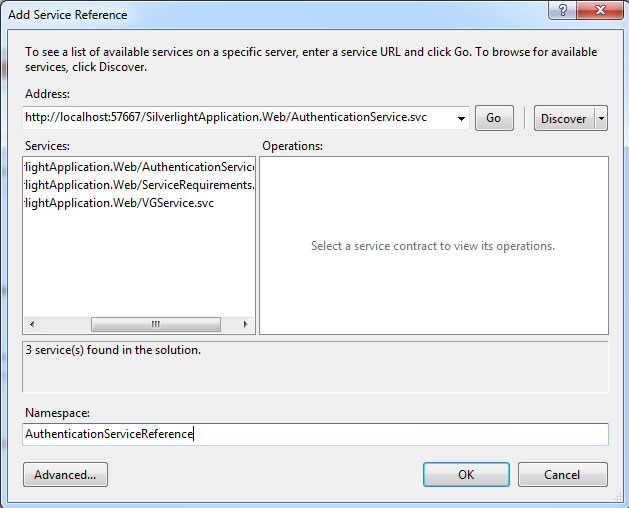
To add the authenetication service to your project you have to:
- Right-click on the project,
- Select "Add service References",
- Put the adress of the Authentication Service,
- Select the service,
- Rename the service,
- Click "OK"
Modify your Login Page
Create your login page in silverlight application containing a username/password textbox and a validation button, and on the validation button put the following code:
AuthenticationServiceClient client = new AuthenticationServiceClient(); client.LoginAsync(userName.Text, PassWord.Password, "", true); //Authenticate the user client.LoginCompleted += new EventHandler <LoginCompletedEventArgs>(client_LoginCompleted);
Use Windows Authentication
Modifying the "app.config" or "web.config" file of your application
To use the windows authentication you have to:
- Configure the authentication mode,
- Configure the HTTModule
Configuring User Name Authentication
<authentication mode="Windows"/>
Configuring VGHTTPModule
cf. Configure VGHTTPModule in the chapter "Use User Name / Password authentication"
Create a service "VGService"
//--------------------------------------------------------
//Methode: GetAllPermission
//This methode is use to have the list of all permissions of the connected user //--------------------------------------------------------
[OperationContract]
public List<VGPermission> getAllPermissions() {
return VGHelper.GetAllPermissions(VGSecurityManager.Runtime.Principal); }
Configure a WCF Silverlight Service
Configure the service in the web.config file
For all services requiring Visual Guard authentication and authorization mechanism, you have to specify the service behavior defined above.
In text editor:
<configuration>
<system.serviceModel>
<services>
<service behaviorConfiguration="VGSecurityBehavior" name="CalculatorService">
<endpoint binding="basicHttpBinding" contract="ICalculatorService" />
</services>
....
</system.serviceModel>
</configuration>
Adding a new service behavior
You have to create a new service behavior and add serviceHostingEnvironment node.
In text editor:
<configuration> <system.serviceModel>
</behaviors> <behavior name="VGServiceBehavior">
<serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled="true" />
<serviceDebug includeExceptionDetailInFaults="false" />
</behavior> </behaviors> </system.serviceModel> </configuration>
Integrating Visual Guard in your WCF Silverlight code
The main class in Visual Guard: Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.VGSecurityManager This class provides the main access point for interacting with Visual Guard. It allows you to set the security of the objects of your application.
There are 3 types of code to integrate Visual Guard:
- When you want to restrict the access of a service to a caller
- When you want to apply security actions on a WebService, a custom class or custom control, you must call Visual Guard to set the security of this object.
- When you want to check if a user has a specific permission or a specific role, in this case you can use Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.VGSecurityManager.Principal .
Restricting the access to a service
Visual Guard is compatible with the standard PrincipalPermissionAttribute class. This attribute will check whether a user is authenticated or is a member of a role. Visual Guard also provides its own attribute: Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.VGPrincipalPermission. This attribute is similar to the standard PrincipalPermissionAttribute class and allows you to check a Visual Guard role or a Visual Guard permission.
The following example demonstrates how to restrict access to the "Multiply" operation to a caller with the permission "CanMultiply".
[C#] [VGPrincipalPermission(SecurityAction.Demand, Name="CanMultiply", Type=VGPermissionType.Permission)] public double Multiply(double n1, double n2) { return n1 * n2; }
[Visual Basic] <VGPrincipalPermission(SecurityAction.Demand, Name:="CanMultiply", Type=VGPermissionType.Permission)> _ Public Function Multiply(Double n1, Double n2) As Double Return n1 * n2 End Function
Securing objects of the application
If you need to apply Visual Guard security actions on the objects of your application, you will need to call Visual Guard to set the security of the object. To do that, you must:
- Add the Novalys.VisualGuard.Security.VGISecurable interface to your class.
- Add the call to the VGSecurityManager.SetSecurity method at the end of the constructor.
If you want to understand how Visual Guard applies the security to the objects of your application, see How Visual Guard secures an application.
The following code shows how to secure the Calculator class that implements the ICalculator service contract:
[C#] public class Calculator: ICalculator, VGISecurable { public Calculator() { // .... // Initialization of the object // .... // This call will indicates to Visual Guard that the class must be secured. VGSecurityManager.SetSecurity(this); } public double Multiply(double n1, double n2) { return n1 * n2; } }
[Visual Basic] Public Class Calculator Implemenents ICalculator, VGISecurable Private Sub New() ' ... ' Initialization of the object ' ... ' This call will indicates to Visual Guard that the class must be secured. VGSecurityManager.SetSecurity(Me) End Sub Public Function Multiply(ByVal n1 as Double, ByVal n2 as Double) As Double Return n1 * n2; End Function End Class
